Boletus: photo, description of the mushroom

On this page, you can look at the photo of what the boletus looks like, read the detailed description of the mushrooms. You will also learn about the distribution halo of some varieties of boletus and twins of these mushrooms.
Content
What does a boletus boletus ordinary look like
Category: edible.
At the species common boletus (Leccinum scabrum) several varieties are distinguished: multi-colored, ash gray, checkerboard (blackening), harsh, gray, pinkish (oxidizing), marsh (white) and black. They differ in the place of growth and the shade of the hat.


In order to get an idea of what the brown boletus trees look like, look at the photo of the mushroom above: the cap of the brown boletus tree (diameter 4-12 cm) is gray, brown or brownish, sometimes almost black. It resembles a swollen pillow in shape.
Leg (diameter 1.5-4 cm): white or grayish, with scales, tapering from bottom to top.
Doubles: inedible gall mushroom (Tylopilus felleus). In order not to confuse these mushrooms, carefully consider the photo of the common boletus:

Its flesh is colored evenly, while the flesh of the bile fungus blushes at the site of a slice or break.
When growing: from late June to early November in the countries of the Eurasian continent, North and South America.
Where can I find: in deciduous forests, usually near birch trees.
Eating: very tasty in any form.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: birch, black-headed. In the tundra, where the common birch tree grows next to dwarf birch trees, it is called the birch birch tree.
What does a marsh boletus boletus look like: photo and description of the mushroom
Category: edible.
Marsh boletus cap (Leccinum holopus) (diameter 6-16 cm): usually light brown, has the shape of a swollen pads, dry to the touch.
According to the description, the leg of the marsh mushroom of the boletus boletus is similar to an ordinary night - its height is 4-12 cm, the color is white or light gray.
Tubular layer: young mushrooms are light, while old mushrooms are rich brown.


Pay attention to the photo: the flesh of the bog marsh is very soft, white in color, which does not change at the place of the cut or break. It does not have a pronounced smell and taste.
Doubles: other birch trees, from which the marsh differs by the place of growth, as well as the inedible bile fungus (Tylopilus felleus) with flesh blushing at the site of the cut.
When growing: from the beginning of July to the end of September in temperate countries of the Eurasian continent.
Where can I find: near marshes and in damp forest places, prefers neighborhood with birches.
Eating: only young mushrooms, and they are very tasty in any form.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
What does a brown boletus look like?
Category: edible.


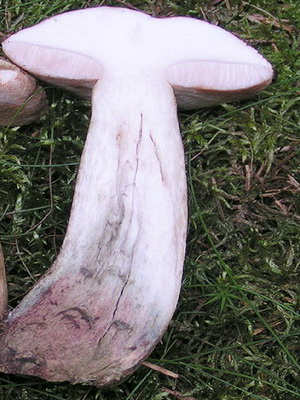
The photo and description of the fungus stiff boletus (Leccinum duriusculum) is somewhat different from the previous species: hat (diameter 5-17 cm): from brown to gray or light purple. It has the shape of the hemisphere, which over time changes to a flatter and pillow-shaped and darkens significantly. Young mushrooms often have scales or pubescence, while old mushrooms are naked and smooth.
Leg (height 6-18 cm): cream below, white above, bluish or light lilac with a noticeable thickening at the very base. Solid, has a cylindrical shape. Often with brownish small scales.
Tubular layer: loose tubes of white color, darken strongly when pressed.
Brown birch trees often grow in a birch-aspen forest.
Pulp: solid, white. On the cut and when interacting with air, it turns pink in the area of the hat, and turns green or turns black at the leg. The taste is sweetish, at the break gives off a pleasant mushroom aroma.
Doubles: are absent.


When growing: from mid-July to early November in temperate countries of the Eurasian continent.
Where can I find: on calcareous soils of deciduous and mixed forests, usually near poplars and aspen trees.
Eating: in any cooked form. The fungus is rarely wormy.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: hard boletus, poplar boletus, stiff oboque.
Mushroom brown cap boletus
Category: edible.


The cap of multicolored boletus (Leccinum variicolor) (diameter 5-12 cm) is gray or brown, with yellow or gray tan marks. It can be brick, orange, beige, pinkish. It has the shape of a hemisphere with a slightly overhanging skin at the edges. In hot weather, it feels dry to the touch, in damp it may be slightly mucous.
Leg (height 9-19 cm): white or light gray, often with small scales. Tapers from bottom to top, has a cylindrical shape. Tubular layer: grayish color.


Pulp: pink in the hat, bluish in the tubular layer, and pink or green in the leg. In young mushrooms, it is dense, with time it becomes more loose. It has a sour smell.
Doubles: are absent.
When growing: from late June to mid-September, it is often found in southern Russia.


Where can I find: in deciduous forests, especially often near birches, oaks and poplars.
Eating: only young mushrooms, as the old ones are tough. In extreme cases, you can use hats. Multi-colored birch bark is very tasty in dried and pickled form.
Application in traditional medicine: not applicable.
Other names: chamomile multi-colored.







