Tinder fungi: a description of the types and healing properties

These fruiting bodies can be found on both living and dead wood. The main harvest season is from mid-spring to late autumn, sometimes winter varieties are also found.
Typically, fungi grow in groups, but there are also individual specimens.
Taste qualities vary. But the most important thing that unites tinder agents of different types is their high healing properties.
Content
What does a birch tinder look like and the beneficial properties of the mushroom
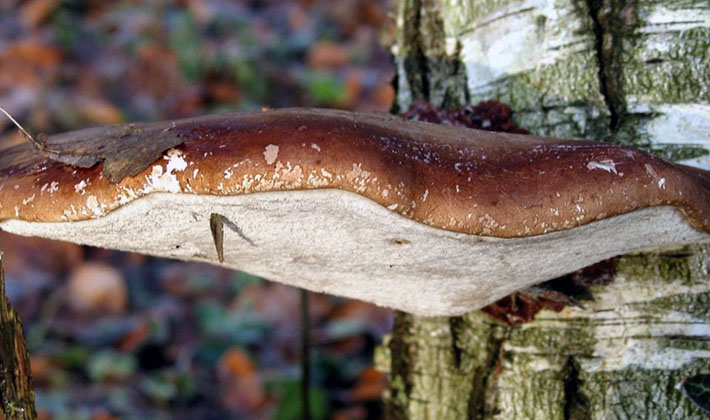

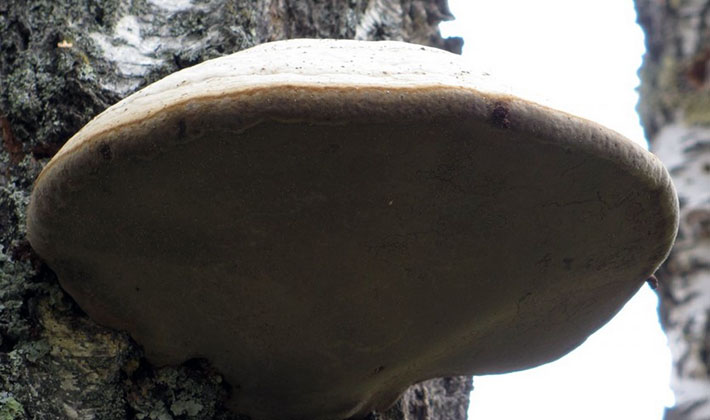
Pipes birch (Piptoporus betulinus) can be observed year round. In winter, they become harder, but do not change their properties. Young light-colored tinder-eaters are suitable for food.
Habitats of birch tinder fungi: in moist forests, on dead wood and birch felling.
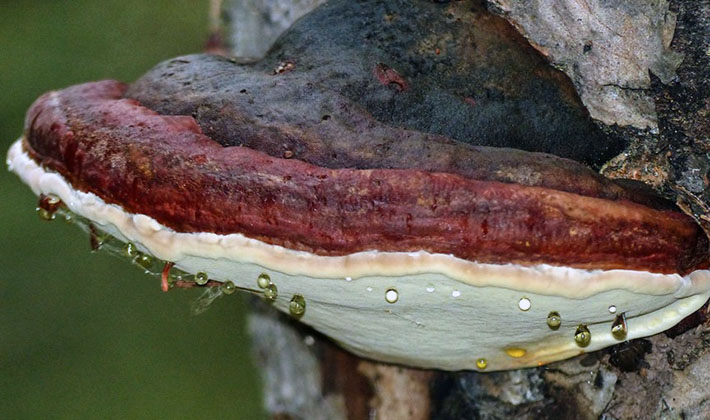

Season: intensive growth - in May-November; in winter, growth slows down significantly, but the properties of the fungus do not change.
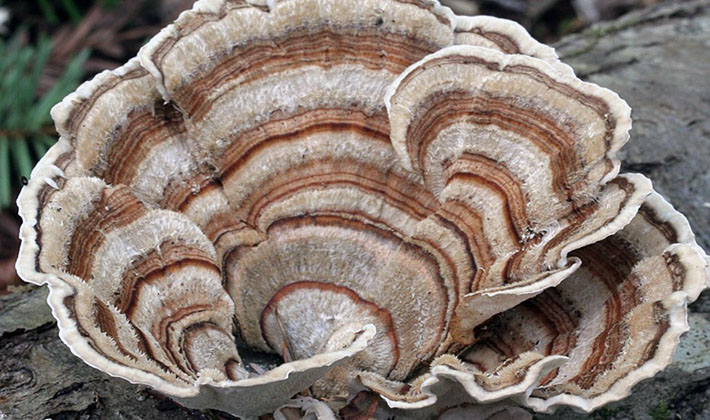
The appearance of the fruit body of the birch tinder fungus is rounded, the mushroom has a small leg. A distinctive feature of the species is a pillow-shaped or flattened-hoof-like, round, kidney-shaped fruit body, slightly convex above, with a blunt, rounded edge. The size of the fruiting body is from 3 to 20 cm, there are specimens up to 30 cm in size, and 2-6 cm thick.
As you can see in the photo, the surface of the fruit body of the fungus mushroom is flat, smooth, covered with a thin, easily detachable film, sometimes there is a cracking skin:
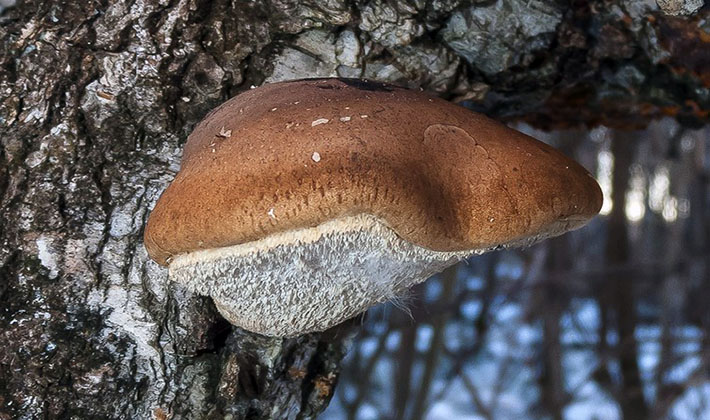
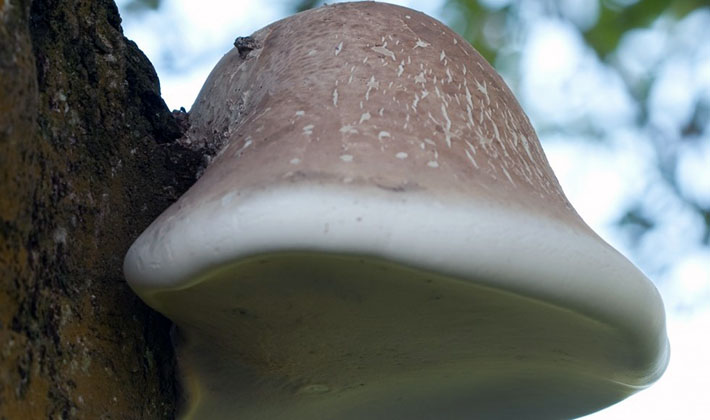
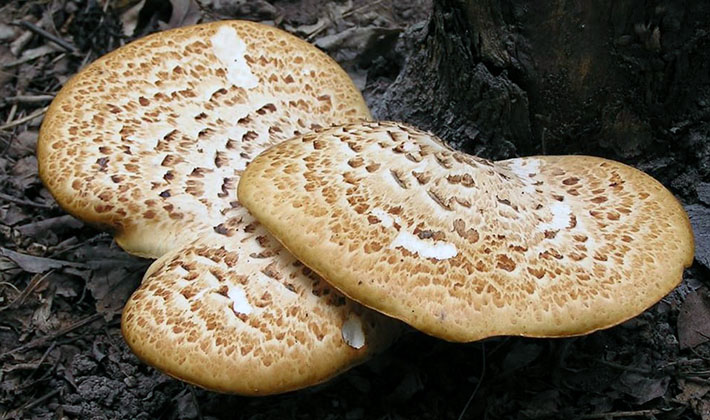



The color of the caps of young mushrooms is whitish or cream, later - yellowish, brown. At the junction with the peduncle, the color of the fruiting body is somewhat darker, with a brown tint.
The tubular hymenophore is up to 10 mm thick; the tubules are white and darken with age. The pores are white, small, rounded or slightly angular, 3-4 of them per 1 mm. Spore powder is white.
Leg or absent, or small, not more than 10% of the length of the fruiting body.
The pulp of a young fungus mushroom looks like a white, soft, homogeneous substance, has a pleasant sour smell. In mature specimens, the flesh is hard, cortical.
Variability: the color of the hat varies from white-cream to brown.
Similar views. The birch tinder, according to the description, is similar to the liverwort mushroom (Fistulina hepatica), which is distinguished by a bright red color.
Edible young and soft mushrooms, 4th category, when the color of the hat is still white or white-cream, they are boiled, cutlets are made.
Therapeutic properties:
- The study of the medicinal properties of the fungus tinder fungus birch in the central nervous system.
- Studies are being carried out on the analgesic properties of these fungi.
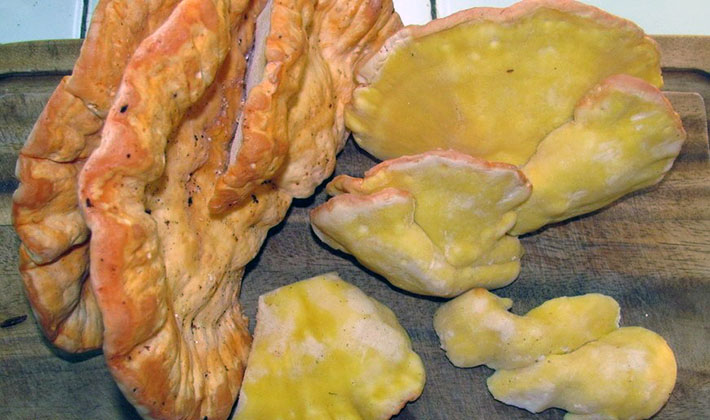
Next, you can familiarize yourself with the photo, a description of the appearance and medicinal properties of sulfur-yellow tinder fungi mushrooms:



Description of the sulfuric yellow tinder
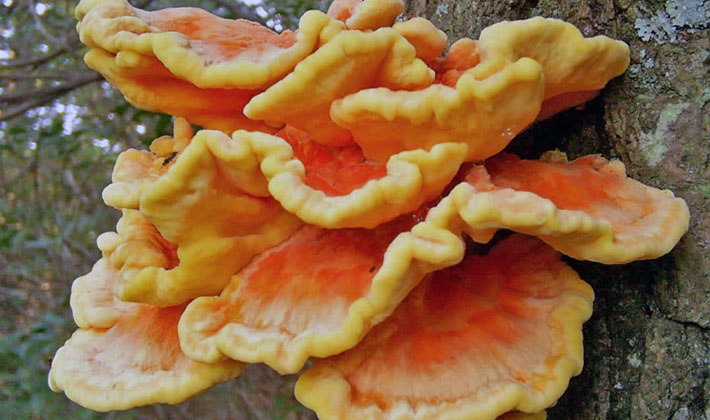

Pipes sulfur-yellow (Laetiporus sulphureus) - One of the most beautiful mushrooms in the warm season. Then they look like thick bright orange and yellow rose petals.In late autumn, tinder fungi of this species age, fade to gray-cream color, and are destroyed. In winter, the remains of this fungus are visible on the trees, and the external state depends on what season was before the onset of frost - dry or wet, and also on the time of growth.
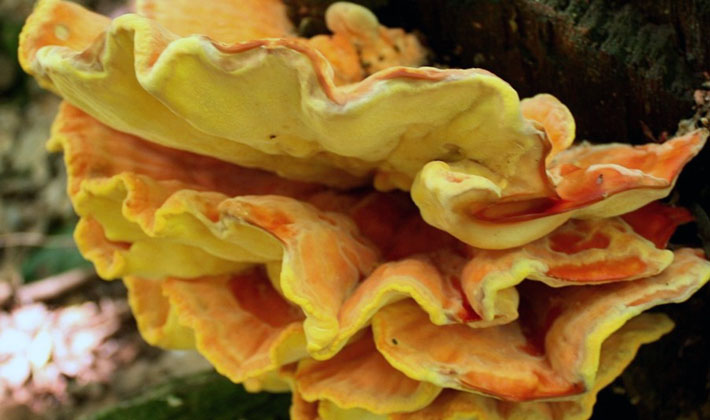

The fact is that the bulk of sulfur-yellow tinder fungus grows early - in June. However, there is a second and third wave of growth until the fall. These autumn waves of mushrooms can remain for the winter. If the frosts are early, then the appearance of the mushrooms may be yellowish. But usually by the beginning of negative temperatures they manage to fade, partially collapse, and in this form they can stay all winter.
The properties of tinder fungi called sulfur yellow in winter are significantly inferior to summer specimens. Nevertheless, in case of urgent need for therapeutic purposes, you can use them in the winter. There is very little information about this in the literature.
Habitats: on rotting oaks, grow in large groups.
Season: May - August, when they are edible, inedible in winter.
The hat. The mushroom has the appearance of a flower with thick and rounded petals.
Pay attention to the photo - a distinctive feature of this type of polypore is the sulfur-yellow and pink-yellow color of fruit bodies of pancake-like or petal shape:
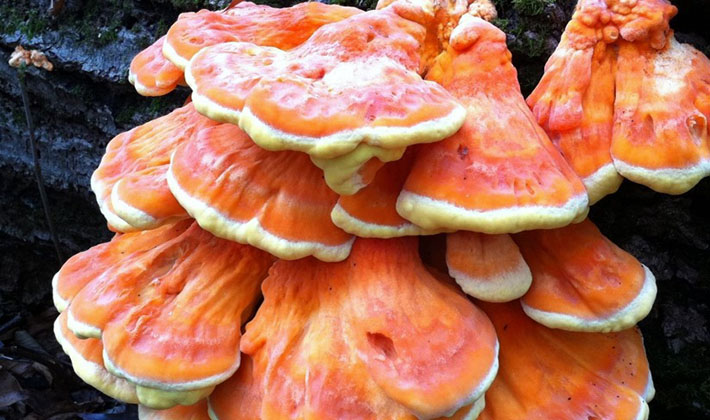
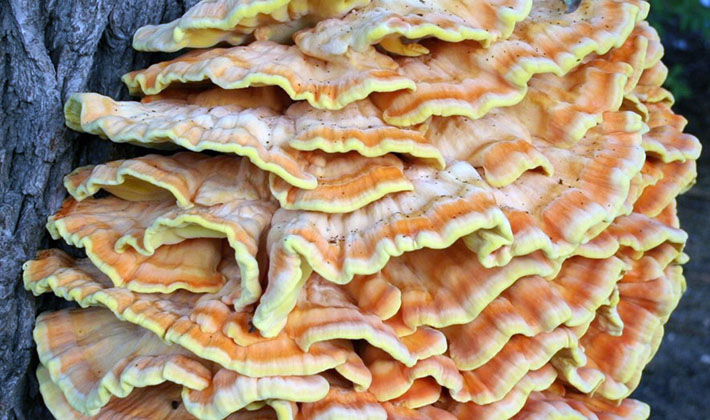
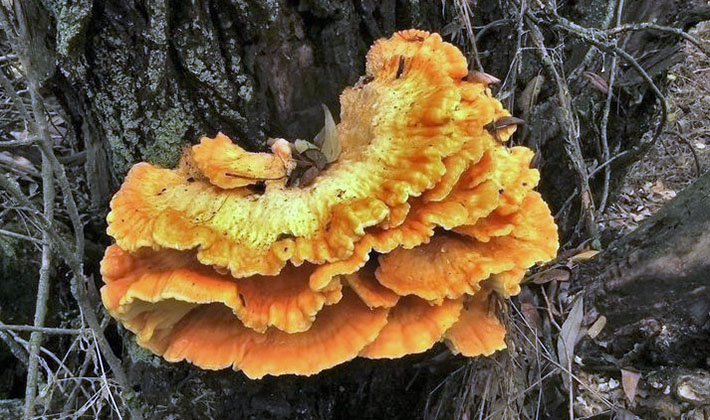



They are attached sideways to the tree and grow tiled or, according to the principle of grapes, in clusters. The size of the fruiting body is significant - from 3 to 30 cm, and the thickness - from 5 to 20 mm.
In the winter, color and appearance change dramatically. Mushrooms fade and become white-gray. The shape also changes, many edges crumble or break.
The tubular layer is finely porous, sulfur-yellow. Spore powder is pale yellow.
Pulp: juicy, pinkish-cream, with a pleasant taste and smell, in old mushrooms, the fabric becomes rubbery and inedible.
Variability: the color of the fruiting body changes as it ripens from sulfur-yellow to pinkish and pink-red, then the mushrooms fade to gray-white and such debris is visible on oaks all winter.
Similar views. The sulfur-yellow tinder is similar in appearance and color to the merging tinder (Albatrellus confluens), which has a tuberous yellowish-orange hat and is distinguished by the presence of a short cylindrical leg of cream-white color.
Edibility: soft and juicy young specimens are edible, they can be boiled, fried, canned. In some southern countries, they are considered delicious mushrooms. Hard and old mushrooms are not edible.
Edible, 3rd category (the youngest and juiciest) and 4th category.
The healing properties of the fungus:
- Sulfur yellow tinder has antibiotic properties against pathogens of various diseases - staphylococci and against harmful bacteria - pullularia.
- This fungus inhibits the growth of many pathogenic bacteria, lowers blood pressure.
- They found dihydromethinolic acid, which is used in research as a substitute for insulin for the treatment of diabetes.
The following section of the article presents a photo, a description of the appearance and medicinal properties of larch fungus mushrooms:
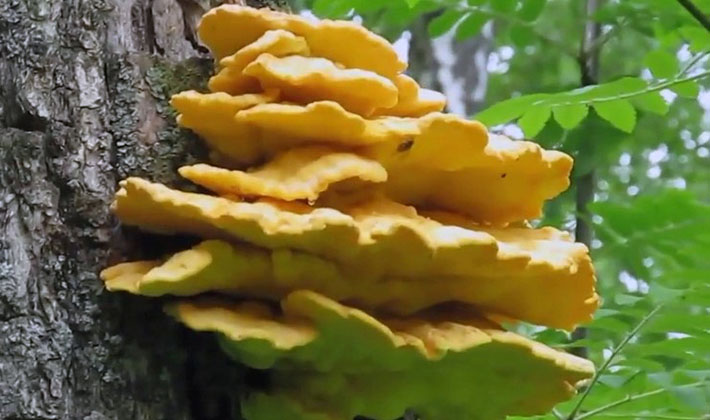
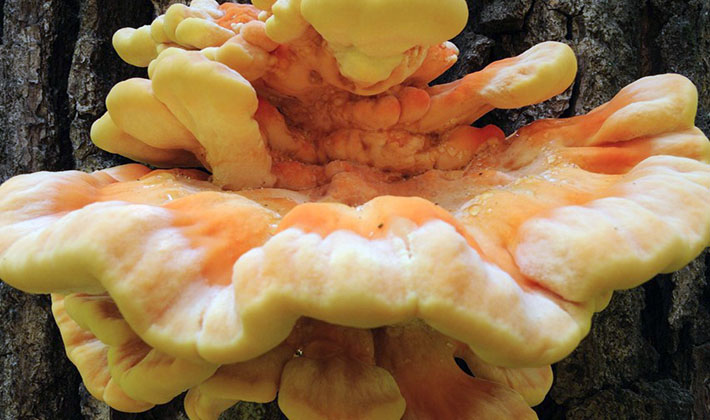


Tinder larch: properties and description
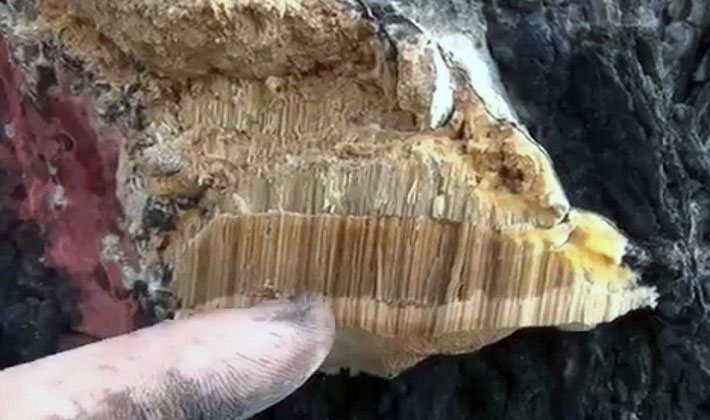

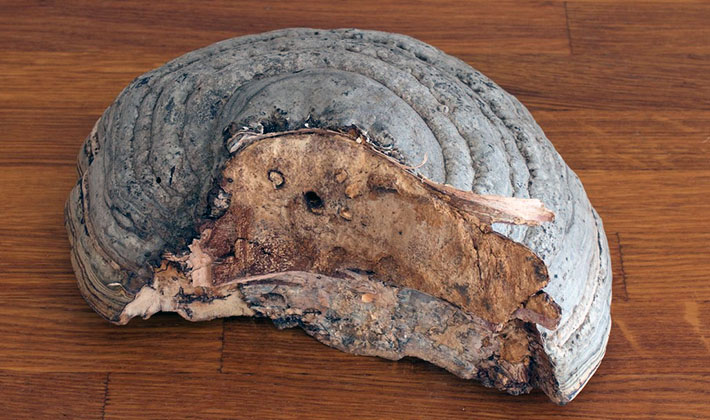
Polypore larch (Fomitopsis officinalis) in winter and summer have a similar appearance. In the summer they grow faster. They can be collected at any time of the year, depending on the properties that they want to use.
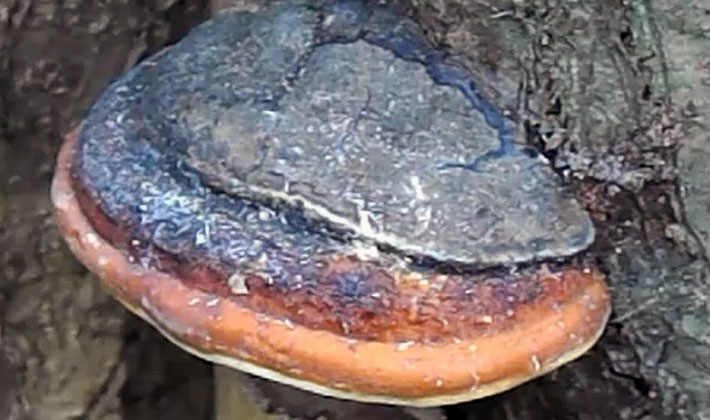

Habitats: on the stumps and dryness of most coniferous and deciduous trees, grow in small groups, or singly.
Season: year-round, long-term view.
The fruit body is perennial, thick, 5-15 cm wide, sometimes specimens up to 30 and 3-15 cm thick are found. The distinctive property of the species is first a kidney-shaped, later hoof-like, cantilever, fruit body grown sideways. The appearance of it is pinkish-brown or light brown with concentric patterns or lines. The surface of the fruiting body is rough, often hilly, covered with a thin, hard, cracking crust. The edges are dull, rounded.
As shown in the photo, the tubular layer of this edible fungus fungus is finely porous, even, whitish-yellowish or light yellowish:
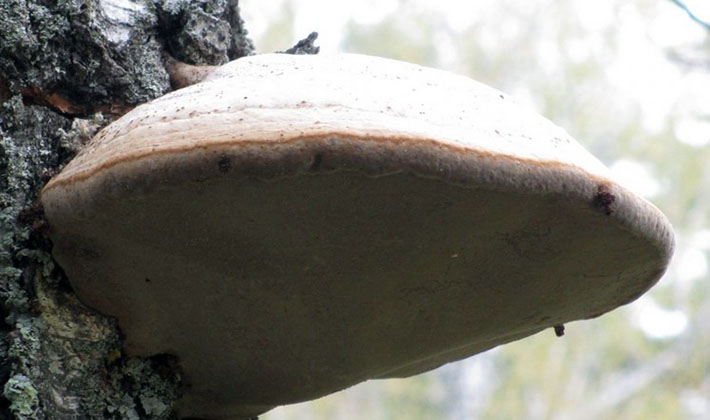
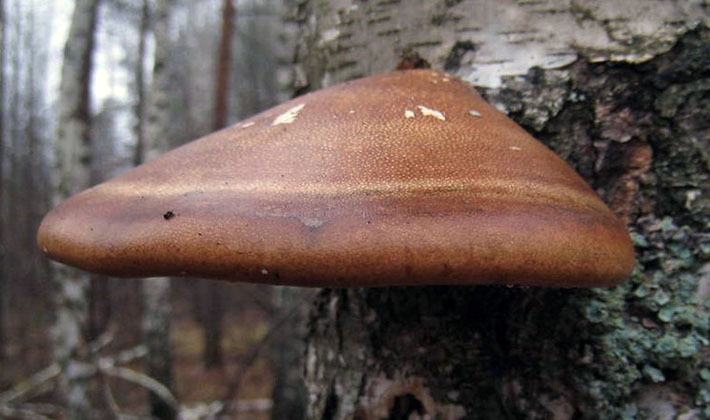
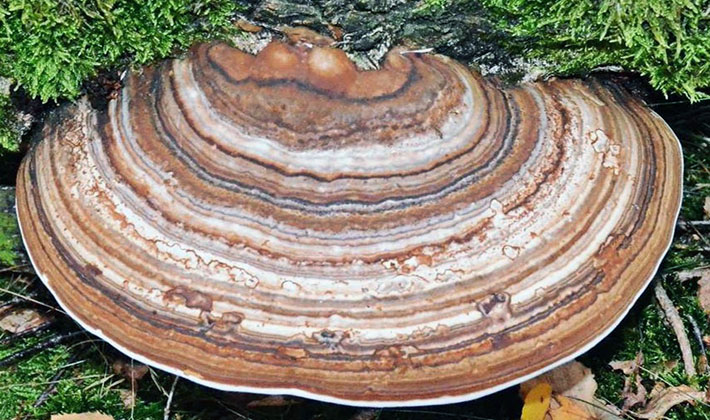



Spore powder is whitish.
Pulp: thick, cork-like, later woody, first whitish, later light yellow, bitter in taste. Over time, the fabric becomes loose and crumbles. The tubes are whitish with a blue tint, later grayish.
Variability: the color of fruiting bodies varies from white-cream to light brown.
Similar views. The larch fungus in shape is similar to the bordered fungus (Fomitopsis officinalis), which is distinguished by a reddish border and yellow-brown color.
Edibility: inedible, but have medicinal properties.
Useful properties of fungus larch fungus:
- From tsarist Russia, several thousand pounds of larch tinderpods were annually exported to Europe, which were used for medicinal purposes, as well as as a dye and for brewing.
- There is a legend about the Greek king Mithridates, whom this miracle mushroom saved from poisoning.
- These mushrooms contain agaricic acid, buricolic acid, lanophil polysaccharide, fumaric, ricinolic, citric and malic acid, as well as other organic acids, fatty oil, phytosterol, glucose and mannitol.
- Another useful property of tinder fungus is its high antitumor effect.
- Larch pants are used to treat hepatitis B and C, hepatoses, fatty liver.
- They are used for complex therapy along with shiitake and reishi for the treatment of pulmonary diseases, including asthma and tuberculosis.
- The small amounts of agaricin in these fungi have a calming and hypnotic effect.
- Mushrooms restore impaired liver secretion of bile and other fat-breaking enzymes.
- A lanophile polysaccharide was isolated from this fungus, which causes a poorly functioning liver to secrete the necessary enzymes and restore impaired metabolism.
- Hemostatic drugs are prepared from the fungus, used as a laxative, treats bruises and asthma with a decoction.
- These mushrooms contain up to 70% of resinous physiologically active substances, such as agaricic acid, which is used for tuberculosis.
- They are used to treat jaundice.
Look at the larch fungus looks in the photo, the description of which is presented above:



The tinder fungus: how it looks and what is useful
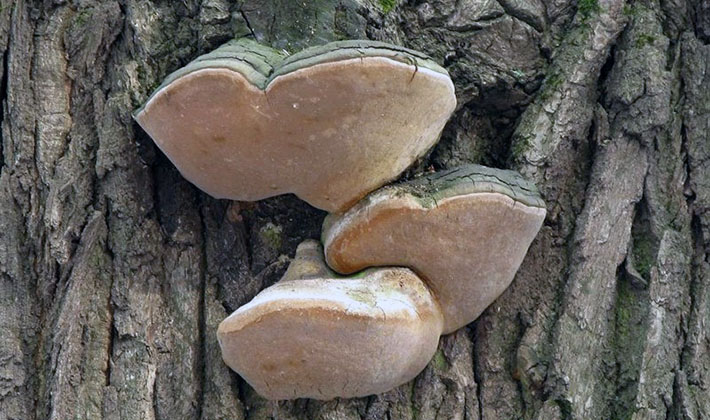

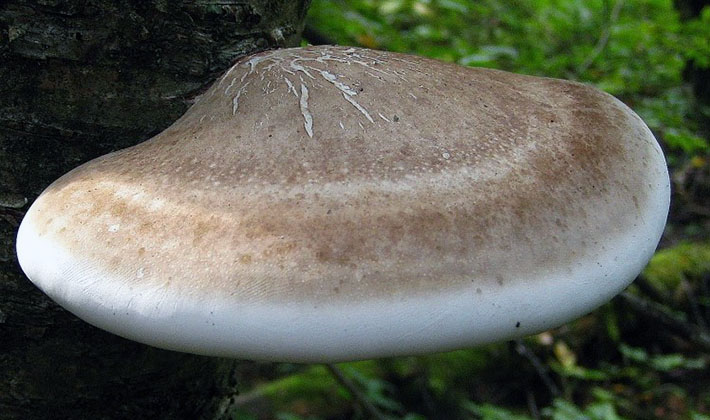
Adult specimens of the tinder fungus (Phellinus igniarius) have a similar look in summer and winter. In the summer they grow faster. They can be collected at any time of the year, depending on the properties that they want to use.
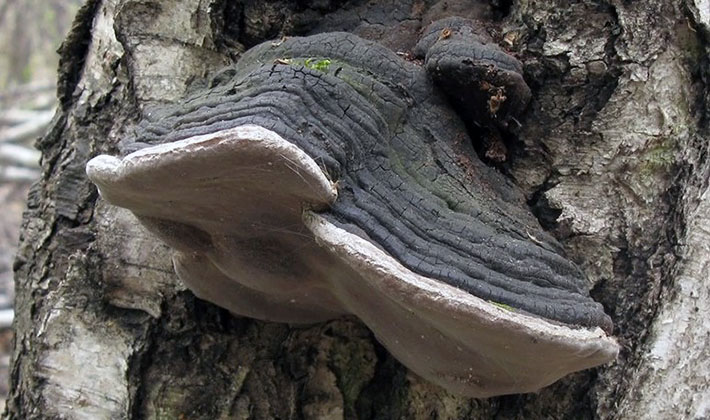

Ghe grows a fungus tinder fungus: on dying trees in mixed forests, most often on the trunks of conifers, they grow in groups or individually.
Season: year-round, long-term view.
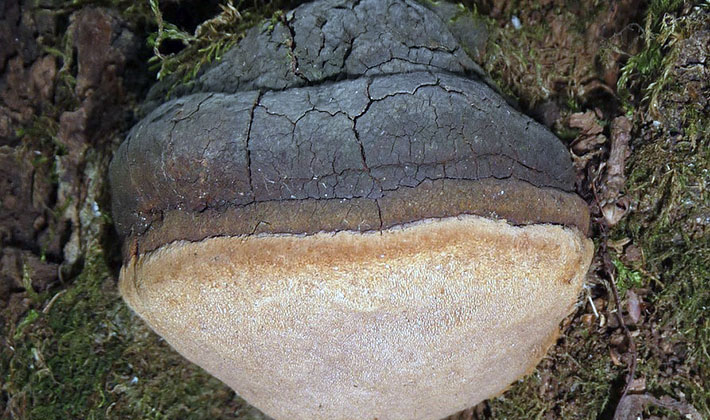
The fruiting bodies of this perennial tinder fungus resemble first hemispheres, later hoof-like ones, seated laterally on wood. The size of the fruit bodies is from 5 to 30 cm, the thickness is from 2 to 12 cm. A distinctive property of the species is the fruit body of a hoof-like shape with two zones. The upper part consists of an almost black or dark gray crust, cracking over time and on which moss or other plants can grow. The second part has a blackish-brown concentric zone. The edges are thick.
The lower side is tubular (tubal hymenophore). The tubes are layered, each year grows from 5 to 6 mm thick. The pores are small, rounded, with solid edges, there are 4-6 pieces per 1 mm. The color of the hymenophore is chestnut or rusty brown.
The flesh is cork-like or woody, hard, dark brown or chestnut brown.
Variability: in a tinder fungus, the false color changes in layers.
Similar views. The false tinder fungus can be confused with the old bordered tinder fungus (Fomitopsis pinicola), which differs not in two, but in three zones on the surface, it still has a red concentric zone, similar to a red border.
The benefits of tinder fungus false indicate its high antibiotic properties.
Where and how does a tinder fungus grow
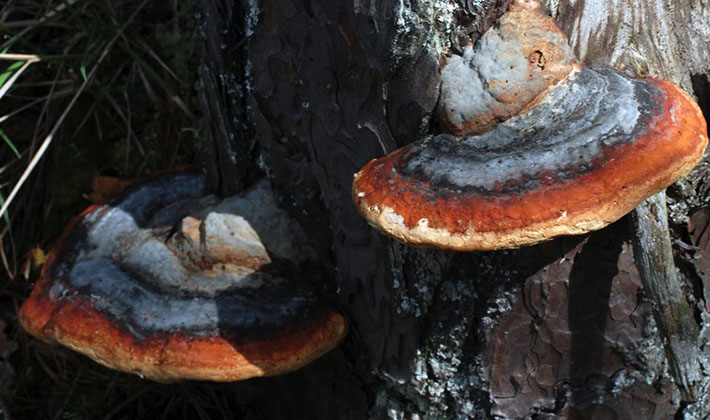

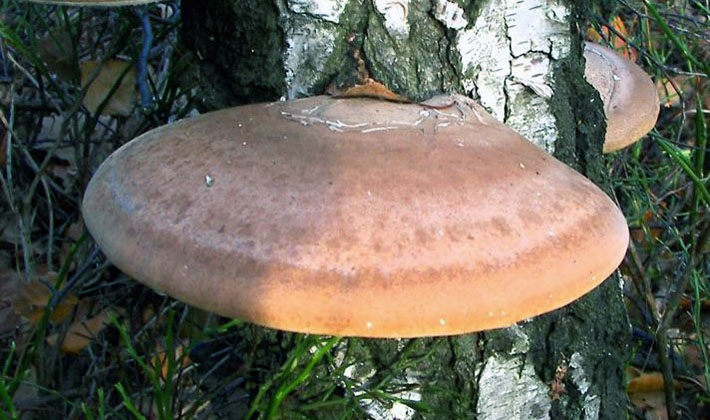
Adult copies of the edged tinder fungus (Fomitopsis pinicola) have a similar look in summer and winter. In the summer they grow faster. They can be collected at any time of the year, depending on the properties that they want to use.
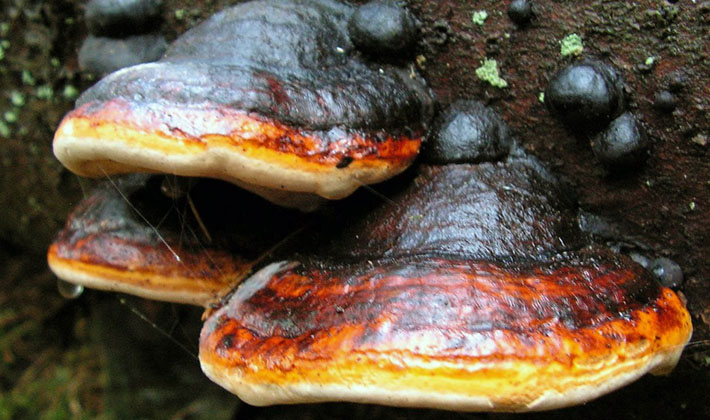

Habitats: on the stumps and dryness of most coniferous and deciduous trees, grow in small groups or individually.
Season: year-round, long-term view.
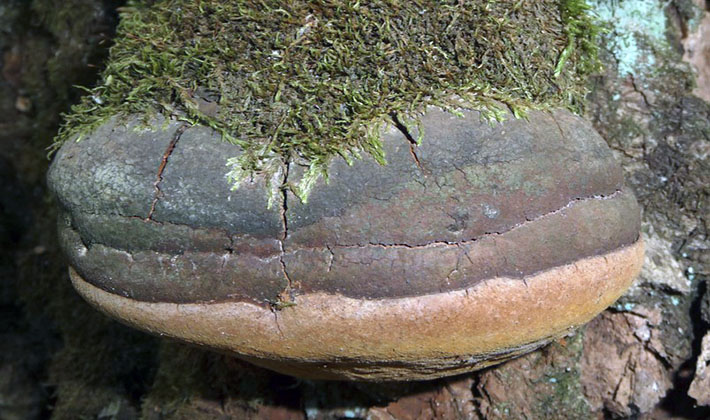
The fruit body is perennial, thick, 5-30 cm wide, sometimes specimens up to half a meter in size and 3-15 cm thick are found. The distinctive property of the species is first a kidney-shaped, later hoof-like, cantilever, side-grown fruit body with bright yellowish-white and reddish concentric zones , with a particularly prominent characteristic yellow-white-red stripe along the edge. The upper surface of the fruit bodies is uneven, furrow-zoned. Young fruiting bodies have the ability to isolate droplets of a colorless liquid that become viscous and hold on the surface.
The tubular layer of this variety of tinder fungus is finely porous, even, whitish-yellowish or creamy yellowish, sometimes with a pink tint. This layer darkens or turns brown when pressed. Spore powder is whitish.
Pulp: thick, cork-like, later woody, first light yellow, later chestnut or brown. The tubes are whitish, later yellowing.
Variability: the color of young fruiting bodies is yellowish-reddish or reddish-buffy, then becomes reddish-brown. In old mushrooms, a black coating, or bark, appears on top.
Similar views. The tinder fungus, bordered at an old age, has a black bark on top, so it becomes like a false tinder (Phellinus igniarius), but is still distinguishable by the characteristic bright yellow-red border near the base.
This variety of tinder fungi is inedible, but these mushrooms have medicinal homeopathic properties.
Pipes bordered everywhere grow in the forests of Russia, in all its parts, in contrast to the larch polypore, which has a complex of healing properties and which is harvested most in Siberia. Therefore, scientists are so interested in exploring the properties of the edged tinder. These studies are ongoing. Currently, preliminary results on the effect and possibility of treatment with tinder fungus extract, bordered by the central nervous system, reducing pain, relieving stress have been obtained.
Other varieties of tinder fungi: May and volatile

Tinder fungus May (Polyporus ciliatus).
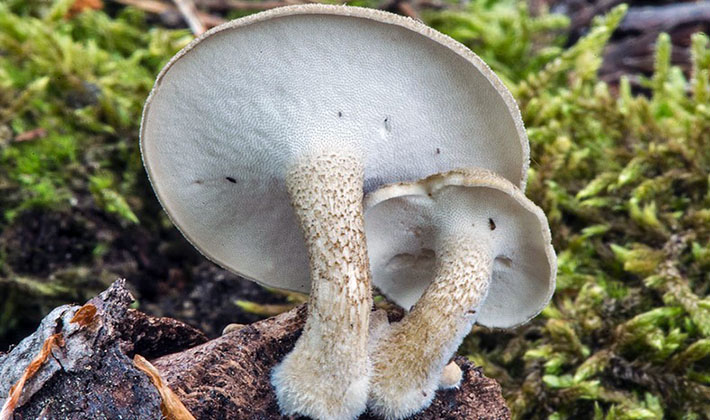

The rough tinder fungus of May grows later: on stumps and fallen trees in forests and gardens, grow in small groups or singly.
Season: May - October.
The hat of this variety of tinder agents has a diameter of 3-10 cm, flat, cream-colored with a felt-scaly surface, with lighter edges, as well as a dark leg.
Leg: dense, cylindrical, 3-9 cm tall, 4-10 mm thick, sometimes curved, covered with dark scales, gray-brown.
The tubular layer has a width of 4-6 mm, contains thin, rounded or angular pores.
Pulp: young mushrooms are white, later cream, with a pleasant mushroom smell.
Variability: the color of the hat varies from cream to light brown, and in old mushrooms to grayish brown.
Similar views. The tinder fungus in May in the shape of the hat and the color of the tubes is similar to the variable fungus (Polyporus drumalis. The main difference between the variable fungus is the gray-brown hat and the brown-black color of the lower part of the leg.
This variety is inedible, since it has a hard flesh.
Variable fungus (Polyporus varius).
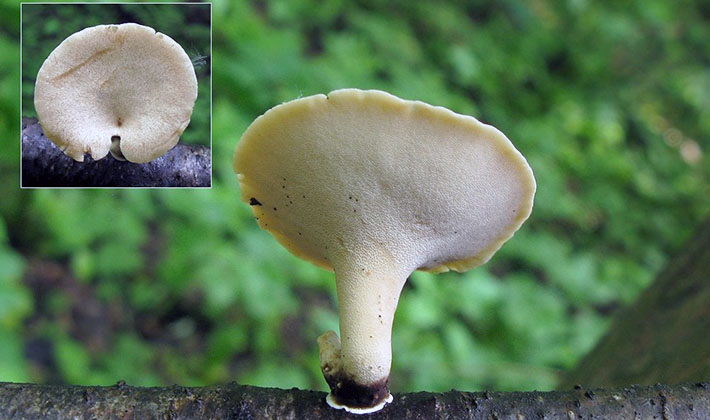

Where the tinder fungus grows: on stumps and fallen forests in forests where there are birch, willow, linden, alder, grow in small groups or individually.
Season: June - November.
The hat of this variety of tinder fungi has a diameter of 3-12 cm. A distinctive property of the species is a linguistic or almost regular round golden yellow funnel-shaped concave hat with wavy edges and an eccentric leg of brown color. The wavy edge of the cap is often divided into blades.The surface of the cap is covered with a thin matte skin, often with a thin radial hatching.
The leg is short, 0.5-3 cm high, 7-15 mm thick, velvety, eccentric, eventually acquires a dark brown or black color in the lower part. The lower part of the leg has a narrowing.
The tubular layer (gimenofor) has a white or light cream color, later light brown. The spores are oblong-elliptical, smooth.
The pulp is hard, first white, later brownish, with a pleasant mushroom smell.
Variability: the color of the hat varies from leather yellow to golden yellow, light brown and tan and almost tobacco.
Similar views. The changeable tinder is similar to the winter tinder (Polyporus brumalis). The main difference between a winter tinder fungus is a gray-brown hat with a depressed middle and a white-cream tubular layer.
This variety is inedible, since it has a hard flesh.
Watch the video, which tells about mushrooms tinder fungi of different types:







