Mushrooms with a round fruit body

Content
Flask mushroom with a round gray hat
Flask lead-gray (Bovista plumbea).
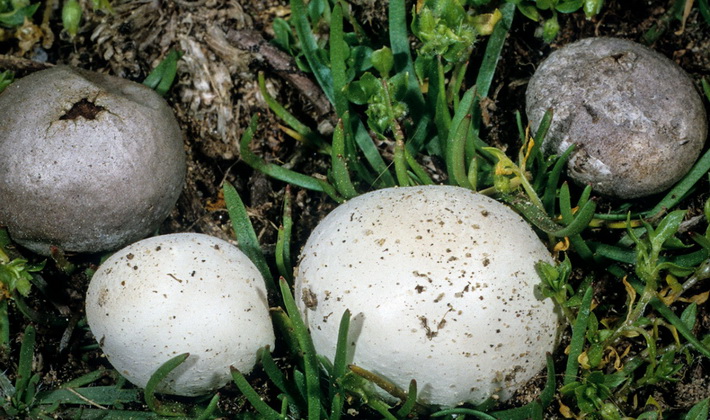

Family: Raincoats (Lycoperdaceae).
Season: June - September.
Growth: single and in groups.
Description:

The fruit body is spherical, white, often dirty.
At the top, a small hole opens with a ragged edge through which spores spread.

The pulp is first white, then grayish, odorless.

Ripening, the cap of a round mushroom (fruit body) becomes gray, dull, with a dense skin.
The mushroom is edible at a young age.
Ecology and distribution:
This mushroom with a round gray hat grows on poor sandy soil, in light forest, on roadsides, in glades and meadows.
Summer and autumn large mushrooms with round fruit bodies
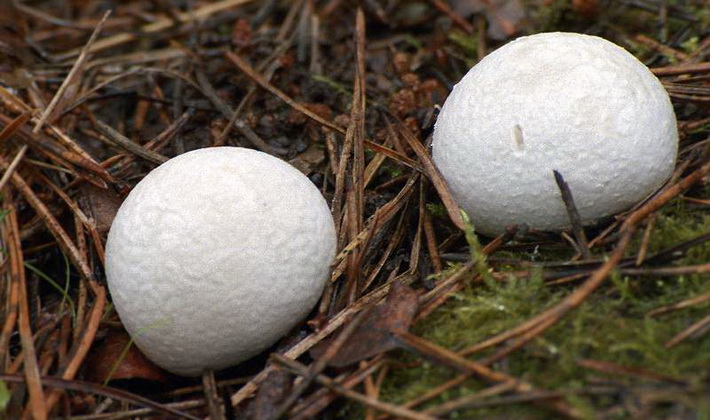
Field raincoat (Vascellum pratense).
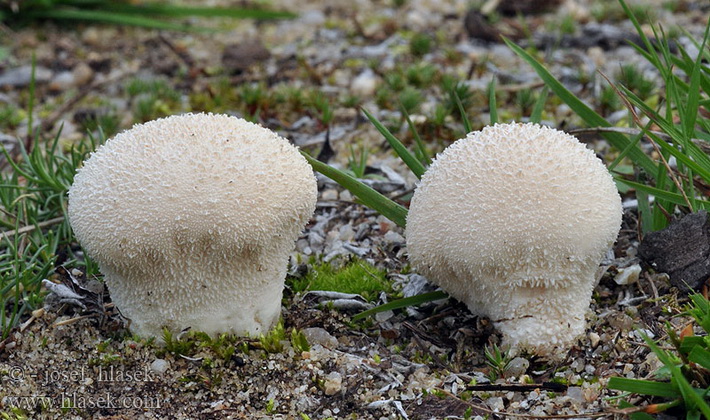

Family: Raincoats (Lycoperdaceae).
Season: summer autumn.
Growth: in small groups, rarely singly.
Description:
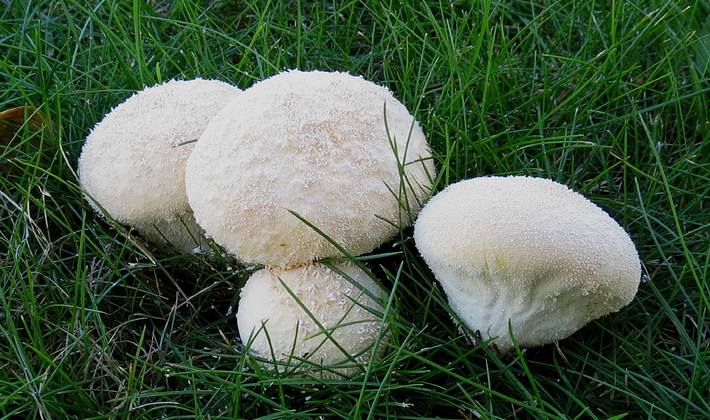

The fruiting body of this large fungus is round, usually with a flattened apex. The transverse septum separates the spore-bearing spherical part from the pedicle-shaped part. Young fruiting bodies are white, then gradually turn light brown.
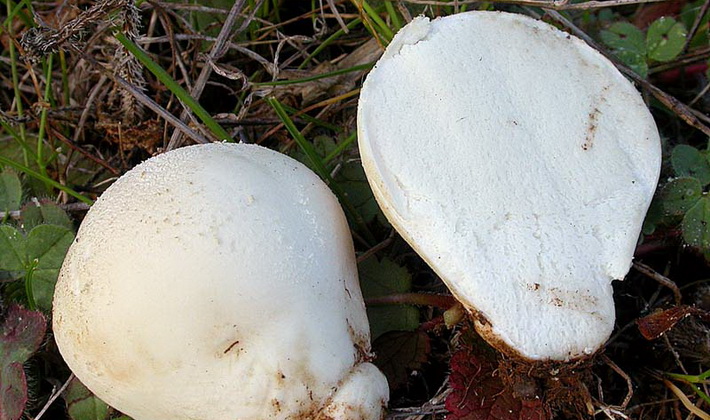

The flesh of the spore-bearing part is first dense, white, then becomes soft, olive.
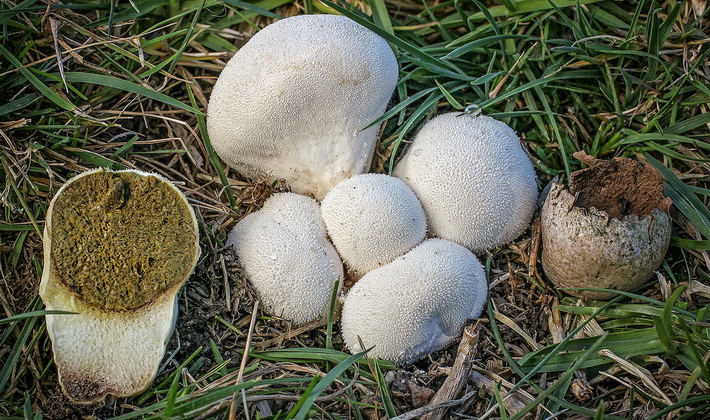

The base is slightly narrowed.
The mushroom is edible at a young age, while the flesh is white. When fried, it tastes like meat.
Ecology and distribution:
Grows on soil and humus in fields, meadows and clearings.
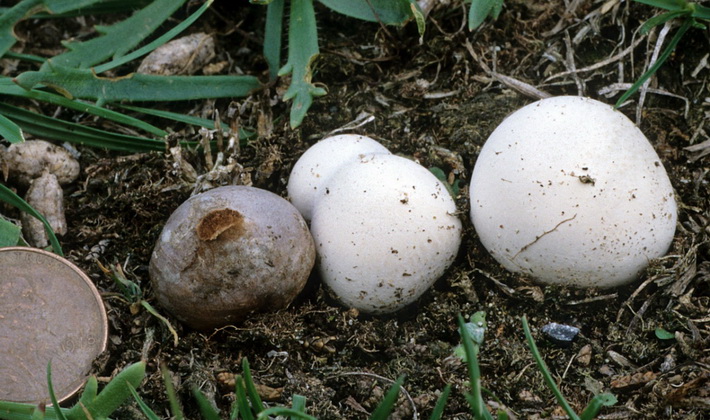
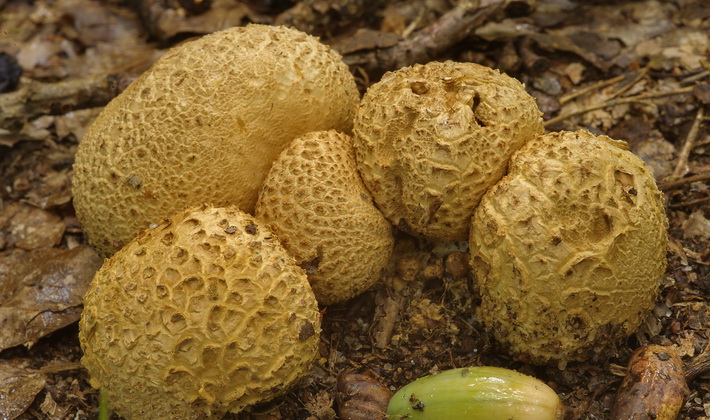
Ordinary raincoat (Scleroderma citrinum).

Family: Pseudo-raincoat (Sclerodermataceae).
Season: July - mid-September.
Growth: single and in groups.
Description:
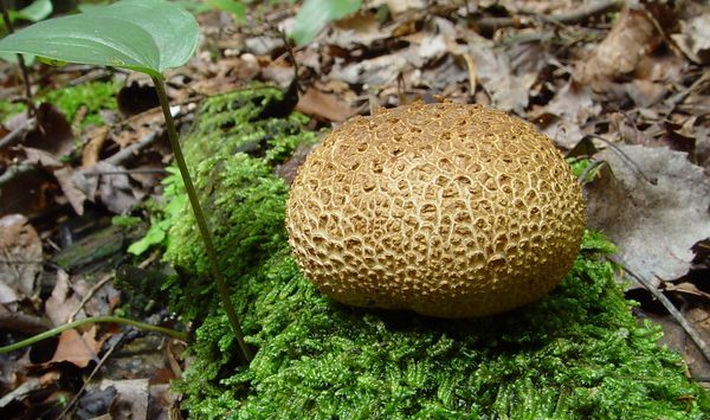

The shell is hard, warty, ocher tones, it turns red at the touch points.
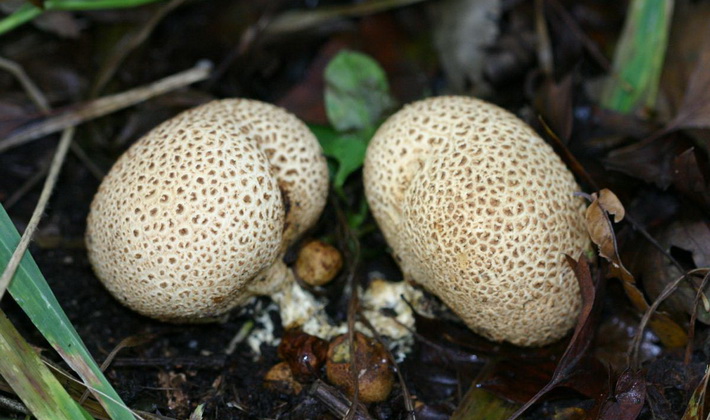

The fruiting body is tuberous or spherical-flattened
Sometimes there is a root-shaped process.
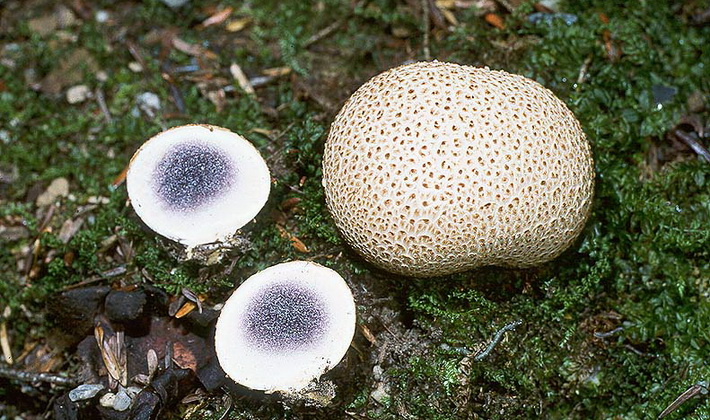

The flesh is light, very dense, whitish, sometimes with a spicy smell, quickly darkens with age to purple-black. The flesh of the lower part always remains white.
This autumn mushroom is inedible, in large quantities, can cause gastrointestinal upset.
Ecology and distribution:
It grows in bright deciduous forests, in young plantings, in rare grass, on bare sandy and clay soil, on roadsides, in glades.
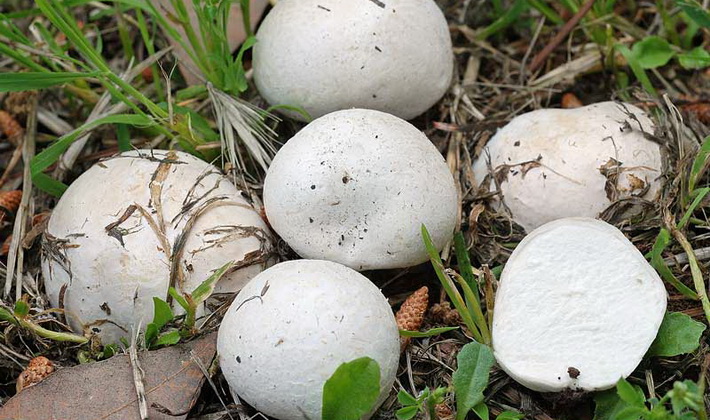
Raincoat giant (Calvatia gigantea).
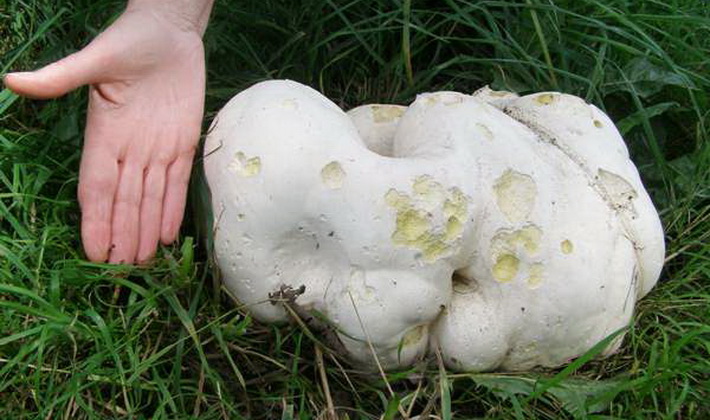

Family: Champignon (Agaricaceae).
Season: May - October.
Growth: single and in groups.
Description:
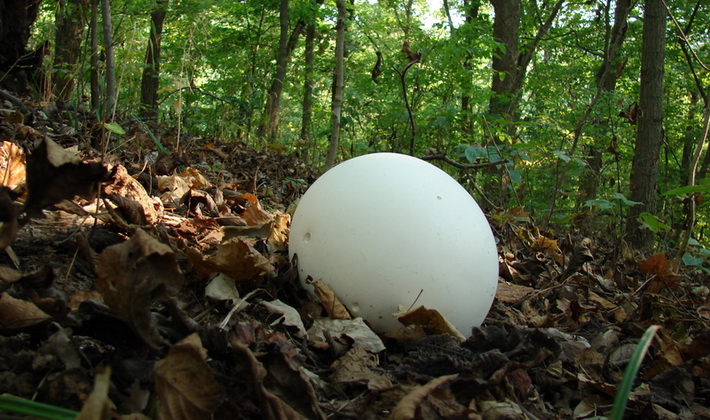

The fruit body is spherical, at first white, turns yellow and turns brown as it ripens. The shell of the ripened mushroom breaks off and falls off.
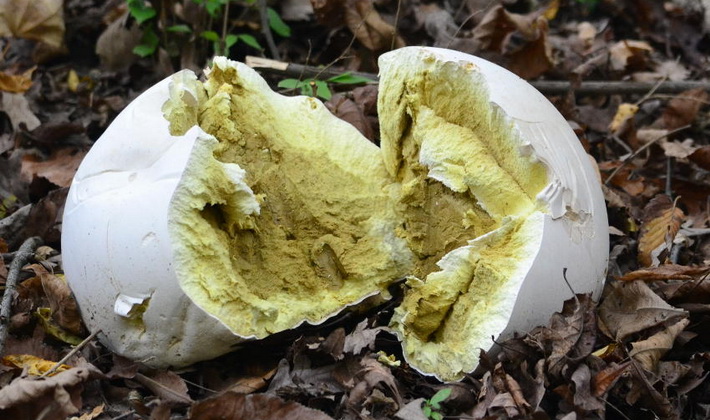

As it ripens, the flesh turns yellow and gradually becomes olive brown.
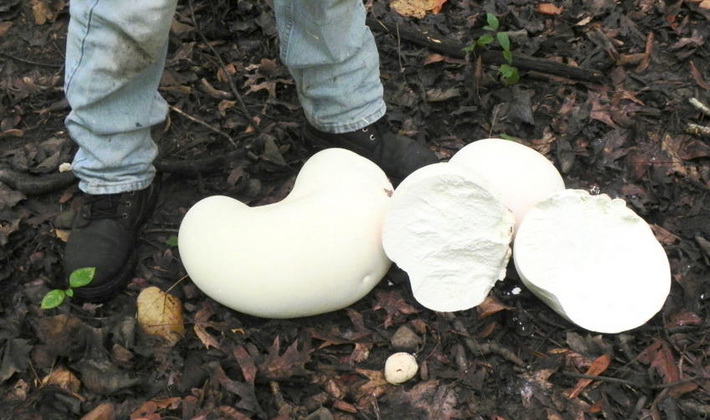

Young mushroom white pulp.
This summer large round white mushroom is edible at a young age, when its flesh is elastic, dense, white. The best way to cook is to slice, pan and fry in oil.
Ecology and distribution:
Grows on the fringes of deciduous and mixed forests, in fields, meadows, in the steppes, in gardens and parks, in pastures. It is rare.
Summer truffle (Tuber aestivum).
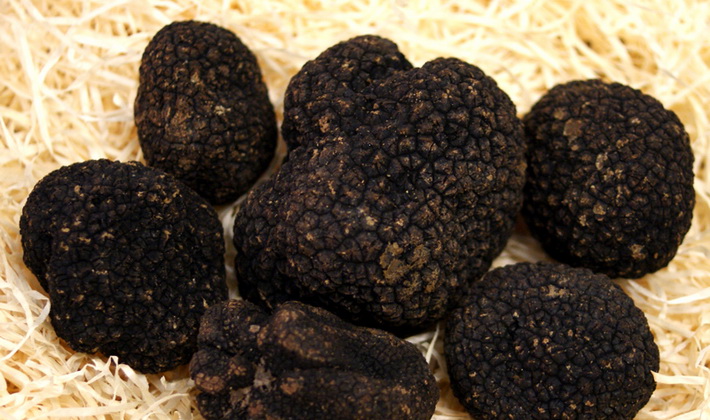

Family: Truffle (Tuberaceae).
Season: summer is the beginning of autumn.
Growth: fruiting bodies underground, usually occur at shallow depths, old mushrooms sometimes appear above the surface
Description:
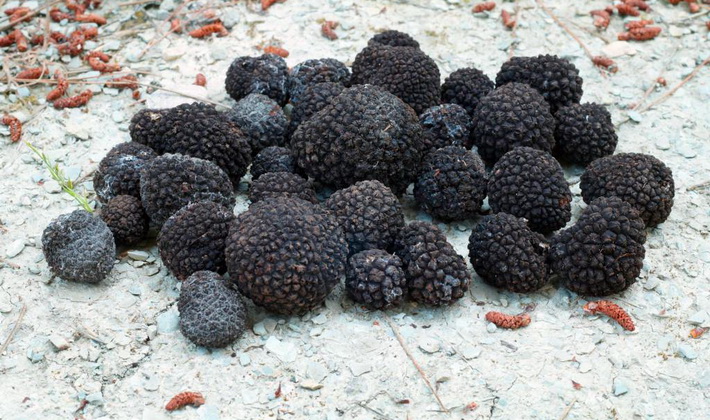

The fruiting body is tuberous or round.
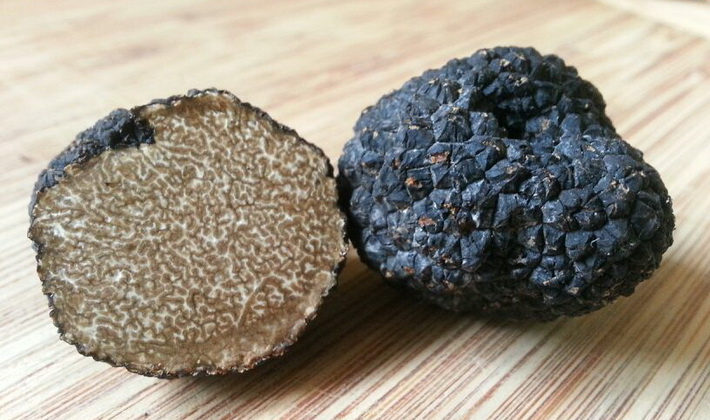

The surface is from brown-black to bluish-black, covered with black pyramidal warts.
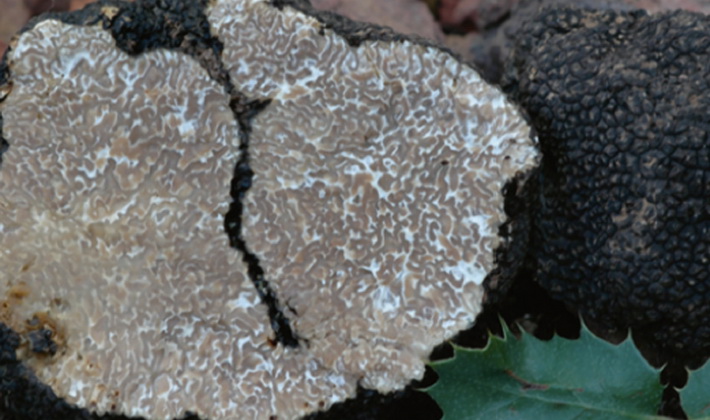

The pulp is very dense at first, in older mushrooms it is more friable, the color changes with age from whitish to brown-yellow. The taste of the pulp is nutty, sweetish, a strong pleasant smell is compared with the smell of algae. Light streaks in the pulp form a marble pattern.
This edible tuberous or round mushroom is considered a delicacy, but is less valued than other real truffles.
Ecology and distribution:
It grows in mixed and deciduous forests in calcareous soils, usually under the roots of oak, beech, hornbeam, and birch. Very rare in coniferous forests. Yellowish flies swarm above the places where truffles grow at sunset. Distributed in Central Europe, in Russia it is found on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus.
Detection: specially trained dogs are used to search for truffles.
Kinds:
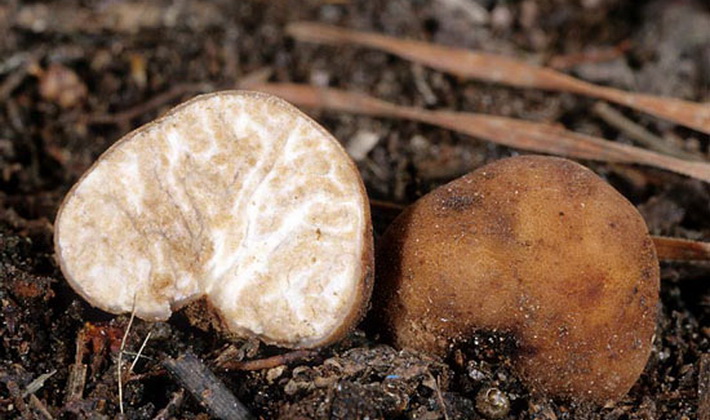

Ginger Truffle (Tuber rufum) distributed in Europe and North America; found in Siberia.
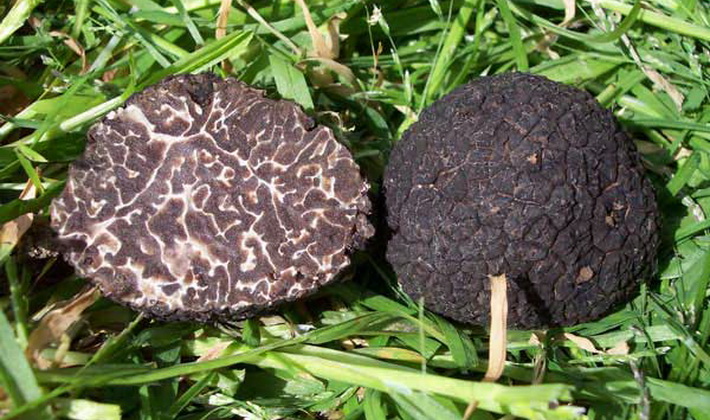

Winter Truffle (Tuber brumale) distributed in France and Switzerland.
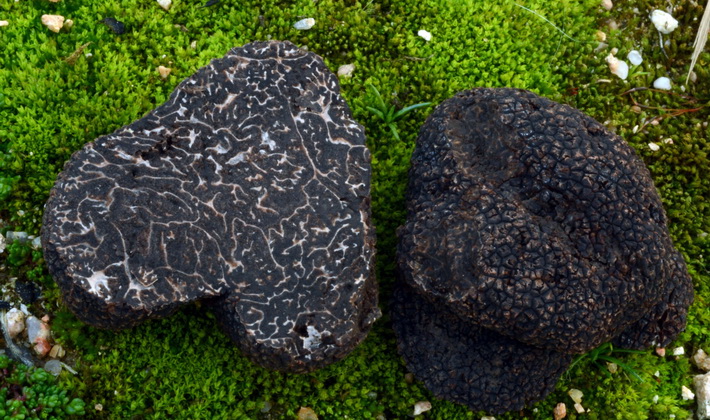

Black Truffle (Tuber melanosporum) - The most valuable truffle. Most often found in France.
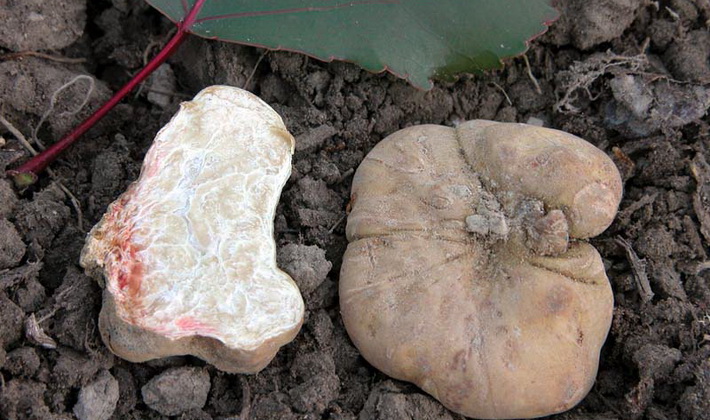
White Truffle (Tuber magnatum) most common in northern Italy and in neighboring areas of France.







